
About
Visual information is one of the most important components in human interface systems. Conventionally, these vision systems consist of CCD cameras and processing units that are implemented at system level. Smart vision chips can be defined as the integration of the image sensor and processing units, which will be more effective solution of visual system implementation. The vision chips would be designed to perform early vision processing such as edge detection, finding the optical derivatives of images for motion detection, and so on. Generally, vision chips have been realized using CMOS process. In consequence of using the CMOS process, we have more freedom in designing signal processing circuitry on a chip. We may choose and devise the suitable photoreceptors with more functionality such as configurable or enhanced sensitivity. Most important change introduced by adapting the CMOS process is readout scheme in view of on-chip processing unit design. For example, photoreceptors can have internal connections with neighbor pixels and some signal processing elements can be attached very near to pixels. These result in the possibility of cost effective parallel architecture design for real-time image processing. Potentially, vision chips can provide more effective solutions of image processing problems.
We have developed a CMOS image sensor with motion detecting capability using frame difference which is a type of vision chips. An analog memory cell for storing the previous frame is implemented in each pixel and the difference between the previously stored frame in the memory and the present frame is used for motion detection. Only moving objects make difference between the frames and stationary backgrounds are suppressed. In addition, the normal video output can be obtained using the presented sensor. The circuitry that computes the position of a moving object is also implemented employing trans-linear analog networks but the part of circuit failed in operation. A demonstration chip has been fabricated using 0.6 mm double-poly, triple-metal CMOS process and consumes 30 mW at 48 frames/s. We presented the image sensor structure of which outputs can be used as preliminary information of motion saliency and tracking servo inputs. Additional normal video output will be desirable to post signal-processing blocks for more complex vision tasks such as segmentation and identification.
We have developed a CMOS image sensor with motion detecting capability using frame difference which is a type of vision chips. An analog memory cell for storing the previous frame is implemented in each pixel and the difference between the previously stored frame in the memory and the present frame is used for motion detection. Only moving objects make difference between the frames and stationary backgrounds are suppressed. In addition, the normal video output can be obtained using the presented sensor. The circuitry that computes the position of a moving object is also implemented employing trans-linear analog networks but the part of circuit failed in operation. A demonstration chip has been fabricated using 0.6 mm double-poly, triple-metal CMOS process and consumes 30 mW at 48 frames/s. We presented the image sensor structure of which outputs can be used as preliminary information of motion saliency and tracking servo inputs. Additional normal video output will be desirable to post signal-processing blocks for more complex vision tasks such as segmentation and identification.
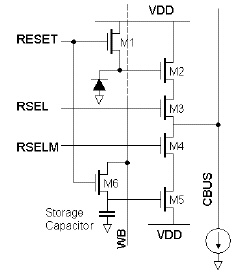
Pixel Schematic
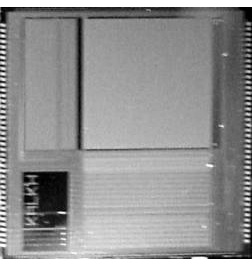 Chip Microphotograph
Chip Microphotograph
 Output
Output
Related Publications
- K.-H. Lee, E. Yoon, "A CMOS Image Sensor With Motion Detecting Function", in IDEC conference summer 2001.




